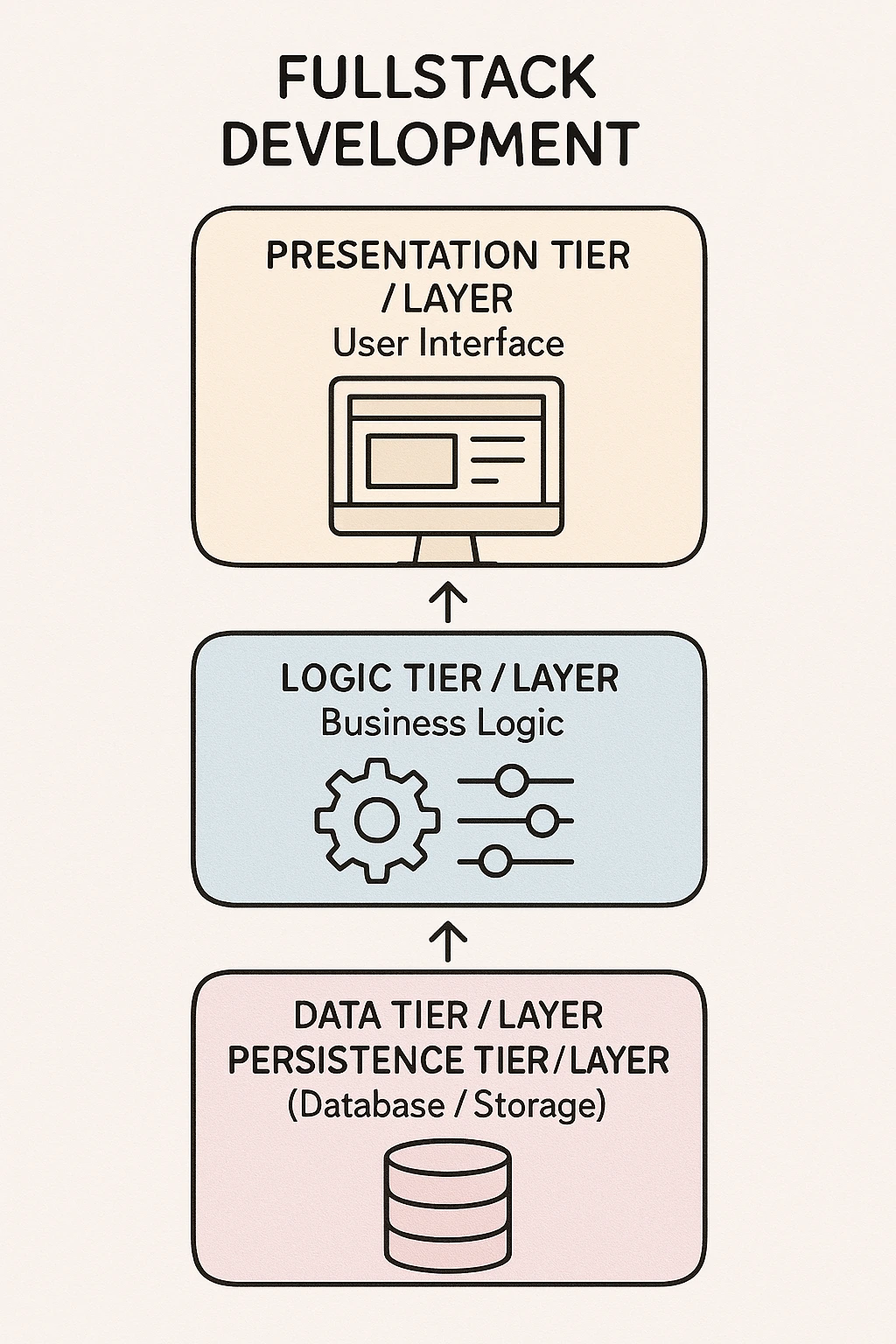
In modern fullstack development, almost all serious applications adopt some form ofmulti-tier architecture(also known asN-Tier Architectureorlayered architecture). We do not cram the UI, business logic, and database access into the same file or single program, but intentionally separate responsibilities into cleartiers (Tiers / Layers)。
The most common and practically recommended is thethree-tier architecture:
Presentation Tier (User Interface)The part that users can see and touch.
- Web front-end (React, Vue, Angular, Next.js, etc.)
- Mobile applications (React Native, Flutter, SwiftUI, etc.)
- Desktop applications (Electron, etc.) Goal: Collect user input, present data beautifully, and provide a good experience.
Logic Tier (Business Logic / Application Layer)The 'brain' of the application.
- Backend servers (Node.js, Spring Boot, Django, .NET, Laravel, Go, etc.)
- Includes: business rules, calculations, validations, permission controls, workflows, third-party integrations Goal: Ensure the program operates correctly according to business requirements.
Data Tier (Persistence Layer / Database and Storage)The place where data is stored long-term.
- Relational databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, etc.)
- NoSQL (MongoDB, Redis, DynamoDB, etc.)
- File storage, caching, message queues Goal: Safely store, read, update, and delete data.
Why use multi-tier architecture? (Main benefits)
Here are the core reasons why professional teams almost universally adopt this layered approach:
- Separation of Concerns— Each layer is responsible for one thing, making the code easier to understand, test, and maintain.
- High maintainability and easy upgrades— Changing the front-end framework (React → Vue) does not require changes to the backend; upgrading the database or changing ORM will not affect the UI.
- Independent scalability— Each layer can bescaled independently.If front-end traffic is high, more front-end instances can be launched; if business logic is complex, the backend can be horizontally scaled; if there is a database bottleneck, read replicas or sharding can be added.
- Team parallel development— Front-end, back-end, and database engineers can work simultaneously with minimal conflicts.
- Code reuse— Business logic and data access layers can be reused by multiple front-ends (Web + App + Admin Backend + Open API).
- Better security— Sensitive logic and database access remain on the server side, and the front end usually cannot connect directly to the database, significantly reducing the attack surface.
- Technical Flexibility— Each layer can use the most suitable technology (React + Java + PostgreSQL, or Vue + Go + MongoDB).
- Easy to Test— Business logic can be unit tested independently without needing a real browser or database; it's easy to mock other layers during integration testing.
Of course, a multi-layer architecture also brings some additional complexity, network latency, and deployment costs. But for medium to large applications, these benefits far outweigh the costs.
In summary:A multi-layer architecture transforms a large and daunting monolithic application into manageable, scalable, and team-friendly components.
The next time you develop a full-stack project (whether it's a simple CRUD or a complex SaaS), start with a three-layer mindset. Your future self and your team will surely thank you for this decision!